十亿级流量下,我与 Redis 时延小突刺的战斗史
一、背景某一日收到上游调用方的反馈,提供的某一个Dubbo接口,每天在固定的时间点被短时间熔断,抛出的异常信息为提供方dubbo线程池被耗尽。当前dubbo接口日请求量18亿次,报错请求94W/天,至此开始了优化之旅。二、快速应急2.1
一、背景
某一日收到上游调用方的反馈,提供的某一个 Dubbo 接口,每天在固定的时间点被短时间熔断,抛出的异常信息为提供方 dubbo 线程池被耗尽。当前 dubbo 接口日请求量 18 亿次,报错请求 94W/天,至此开始了优化之旅。
二、快速应急
2.1 快速定位
首先进行常规的系统信息监控(机器、JVM 内存、GC、线程),发现虽稍有突刺,但都在合理范围内,且跟报错时间点对不上,先暂时忽略。
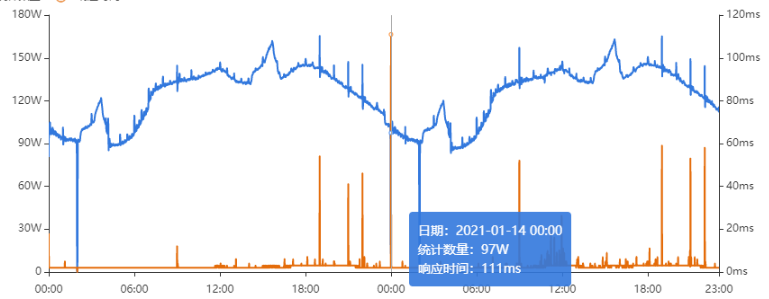
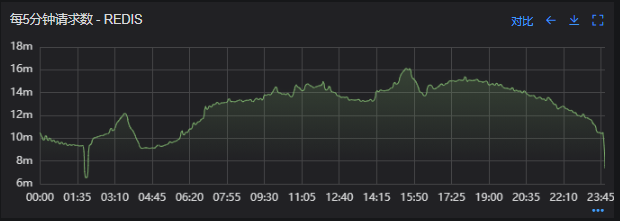
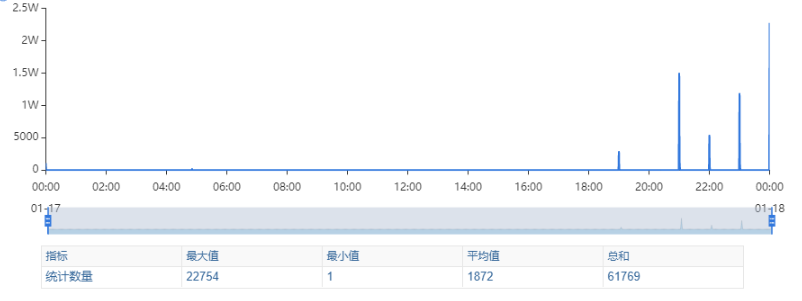
其次进行流量分析,发现每天固定时间点会有流量突增的情况,流量突增的点跟报错的时间点也吻合,初步判断为短时大流量导致。
流量趋势
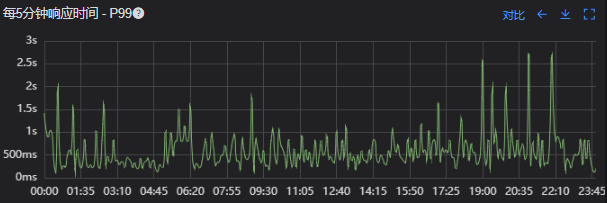
接口 99 线
3.1.2 流程分析
收到请求后调用下游接口,使用 hystrix 熔断器,熔断时间为 500MS;
根据下游接口返回的数据,进行详情数据的封装,第一步先到本地缓存中获取,如果本地缓存没有,则从 Redis 进行回源,Redis 中无则直接返回,异步线程从数据库进行回源。
如果第一步调用下游接口异常,则进行数据兜底,兜底流程为先到本地缓存中获取,如果本地缓存没有,则从 Redis 进行回源,Redis 中无则直接返回,异步线程从数据库进行回源。
3.2 性能瓶颈点排查
3.2.1 下游接口服务耗时比较长
调用链显示,虽然下游接口的 P99 线在峰值流量时存在突刺,超出 1S,但因为熔断超时的设置(熔断时间 500MS,coreSize&masSize=50,下游接口平均耗时 10MS 以下),判断下游接口不是问题的关键点,为进一步排除干扰,在下游服务存在突刺时能快速失败,调整熔断时间为 100MS,dubbo 超时时间 100MS。
3.2.2 获取详情本地缓存无数据,Redis 回源
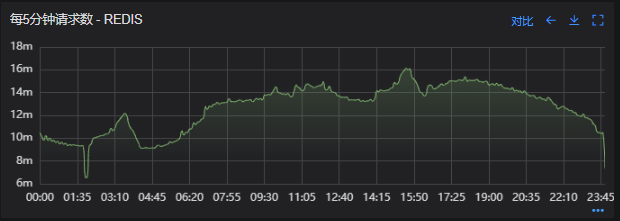
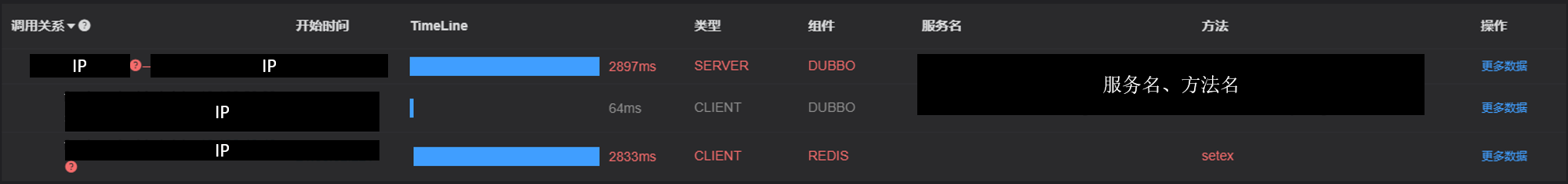
借助调用链平台,第一步分析 Redis 请求流量,以此来判断本地缓存的命中率,发现 Redis 的流量是接口流量的 2 倍,从设计上来说不应该出现这个现象。开始代码 Review,发现在有一处逻辑出现了问题。
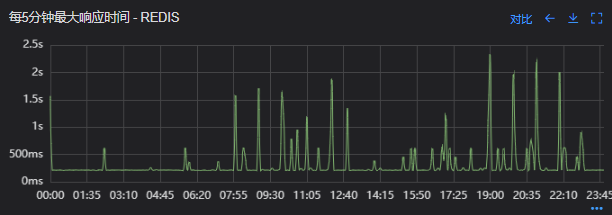
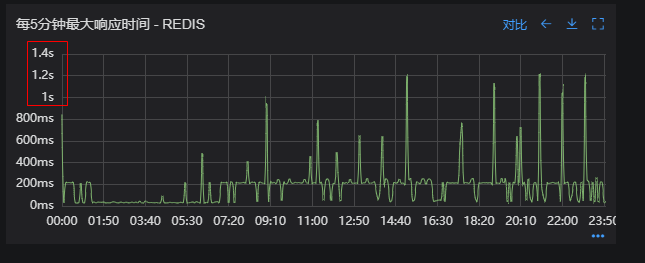
没有从本地缓存读取,而是直接从 Redis 中获取了数据,Redis 最大响应时间也确实发现了不合理的突刺,继续分析发现 Redis 响应时间和 Dubbo99 线突刺情况基本一致,感觉此时已经找到了问题的原因,心中暗喜。
Redis 请求流量
Dubbo99 线
3.2.3 获取兜底数据本地缓存无数据,Redis 回源
正常
3.2.4 记录请求结果入 Redis
因为当前 Redis 做了资源隔离,且未在 DB 后台查询到慢日志,此时分析导致 Redis 变慢的原因有很多,不过其他的都被主观忽略了,注意力都在请求 Redis 流量翻倍的问题上了,故优先解决 3.2.2 中的问题。
四、解决方案
4.1 3.3.2 中定位的问题上线
上线前 Redis 请求量
上线后 Redis 流量翻倍问题得到解决,Redis 最大响应时间突刺有所缓解,但依旧没能彻底解决,说明大流量查询不是最根本的原因。
redis 最大响应时间(上线前)
4.2 Redis 扩容
在 Redis 异常流量问题解决后,问题并未得到彻底解决,此时能做的就是静下心来,仔细去梳理导致 Redis 慢的原因,思路主要从以下三个方面:
-
出现了慢查询
-
Redis 服务出现性能瓶颈
-
客户端配置不合理
基于以上思路,一个个的进行排查;查询 Redis 慢查询日志,未发现慢查询。
借用调用链平台详细分析慢的 Redis 命令,没有了大流量导致的慢查询的干扰,问题定位流程很快,大量的耗时请求在 setex 方法上,偶尔出现查询的慢请求也都是在 setex 方法之后,根据 Redis 单线程的特性判断 setex 是 Redis99 线突刺的元凶。找到具体语句,定位到具体业务后,首先申请扩容 Redis,由 6 个 master 扩到 8 个 master。
Redis 扩容前
从结果上看,扩容基本上没有效果,说明 redis 服务本身不是性能瓶颈点,此时剩下的一个就是客户端相关配置了。
4.3 客户端参数优化
4.3.1 连接池优化
Redis 扩容没有效果,针对客户端可能出现的问题,此时怀疑的点有两个方向。
第一个是客户端在处理 Redis 集群模式时,对连接的管理上存在 BUG,第二个是连接池参数设置不合理,此时源码分析和连接池参数调整同步进行。
4.3.1.1 判断客户端连接管理上是否有 BUG
在分析完,客户端处理连接池的源码后,没有问题,跟预想一致,按照槽位缓存连接池,第一个假设被排除,源码如下。
1、setEx
public String setex(final byte[] key, final int seconds, final byte[] value) {
return new JedisClusterCommand<String>(connectionHandler, maxAttempts) {
@Override
public String execute(Jedis connection) {
return connection.setex(key, seconds, value);
}
}.runBinary(key);
}
2、runBinary
public T runBinary(byte[] key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new JedisClusterException("No way to dispatch this command to Redis Cluster.");
}
return runWithRetries(key, this.maxAttempts, false, false);
}
3、runWithRetries
private T runWithRetries(byte[] key, int attempts, boolean tryRandomNode, boolean asking) {
if (attempts <= 0) {
throw new JedisClusterMaxRedirectionsException("Too many Cluster redirections?");
}
Jedis connection = null;
try {
if (asking) {
// TODO: Pipeline asking with the original command to make it
// faster....
connection = askConnection.get();
connection.asking();
// if asking success, reset asking flag
asking = false;
} else {
if (tryRandomNode) {
connection = connectionHandler.getConnection();
} else {
connection = connectionHandler.getConnectionFromSlot(JedisClusterCRC16.getSlot(key));
}
}
return execute(connection);
}
4、getConnectionFromSlot
public Jedis getConnectionFromSlot(int slot) {
JedisPool connectionPool = cache.getSlotPool(slot);
if (connectionPool != null) {
// It can't guaranteed to get valid connection because of node
// assignment
return connectionPool.getResource();
} else {
renewSlotCache(); //It's abnormal situation for cluster mode, that we have just nothing for slot, try to rediscover state
connectionPool = cache.getSlotPool(slot);
if (connectionPool != null) {
return connectionPool.getResource();
} else {
//no choice, fallback to new connection to random node
return getConnection();
}
}
}
4.3.1.2 分析连接池参数
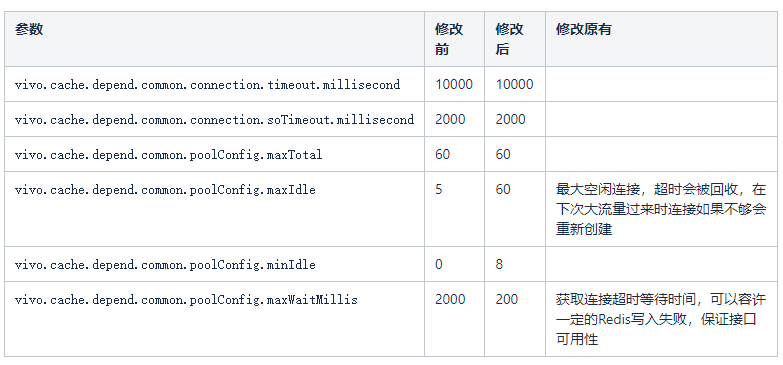
通过跟中间件团队沟通,以及参考 commons-pool2 官方文档修改如下;
参数优化后接口报错量
分析上图发现,确实在几个时间点(9:00,12:00,19:00…),redis 连接数存在上涨情况,跟 Redis 突刺时间基本吻合。感觉(之前的各种尝试后,已经不敢用确定了)问题到此定位清晰(在突增流量过来时,连接池可用连接满足不了需求,会创建连接,造成请求等待)。
此时的想法是在服务启动时就进行连接池的创建,尽量减少新连接的创建,修改连接池参数 vivo.cache.depend.common.poolConfig.minIdle,结果竟然无效???
啥都不说了,开始撸源码,jedis 底层使用的是 commons-poll2 来管理连接的,查看项目中使用的 commons-pool2-2.6.2.jar 部分源码;
CommonPool2 源码
public GenericObjectPool(final PooledObjectFactory<T> factory,
final GenericObjectPoolConfig<T> config) {
super(config, ONAME_BASE, config.getJmxNamePrefix());
if (factory == null) {
jmxUnregister(); // tidy up
throw new IllegalArgumentException("factory may not be null");
}
this.factory = factory;
idleObjects = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(config.getFairness());
setConfig(config);
}
竟然发现没有初始化连接的地方,开始咨询中间件团队,中间件团队给出的源码(commons-pool2-2.4.2.jar)如下,方法执行后多了一次 startEvictor 方法的调用?
1、初始化连接池
public GenericObjectPool(PooledObjectFactory<T> factory,
GenericObjectPoolConfig config) {
super(config, ONAME_BASE, config.getJmxNamePrefix());
if (factory == null) {
jmxUnregister(); // tidy up
throw new IllegalArgumentException("factory may not be null");
}
this.factory = factory;
idleObjects = new LinkedBlockingDeque<PooledObject<T>>(config.getFairness());
setConfig(config);
startEvictor(getTimeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis());
}
为啥不一样???开始检查 Jar 包,版本不一样,中间件给出的版本是在 V2.4.2,项目实际使用的是 V2.6.2,分析 startEvictor 有一步逻辑正是处理连接池预热逻辑。
Jedis 连接池预热
1、final void startEvictor(long delay) {
synchronized (evictionLock) {
if (null != evictor) {
EvictionTimer.cancel(evictor);
evictor = null;
evictionIterator = null;
}
if (delay > 0) {
evictor = new Evictor();
EvictionTimer.schedule(evictor, delay, delay);
}
}
}
2、class Evictor extends TimerTask {
/**
* Run pool maintenance. Evict objects qualifying for eviction and then
* ensure that the minimum number of idle instances are available.
* Since the Timer that invokes Evictors is shared for all Pools but
* pools may exist in different class loaders, the Evictor ensures that
* any actions taken are under the class loader of the factory
* associated with the pool.
*/
@Override
public void run() {
ClassLoader savedClassLoader =
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
try {
if (factoryClassLoader != null) {
// Set the class loader for the factory
ClassLoader cl = factoryClassLoader.get();
if (cl == null) {
// The pool has been dereferenced and the class loader
// GC'd. Cancel this timer so the pool can be GC'd as
// well.
cancel();
return;
}
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
// Evict from the pool
try {
evict();
} catch(Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
} catch(OutOfMemoryError oome) {
// Log problem but give evictor thread a chance to continue
// in case error is recoverable
oome.printStackTrace(System.err);
}
// Re-create idle instances.
try {
ensureMinIdle();
} catch (Exception e) {
swallowException(e);
}
} finally {
// Restore the previous CCL
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(savedClassLoader);
}
}
}
3、 void ensureMinIdle() throws Exception {
ensureIdle(getMinIdle(), true);
}
4、 private void ensureIdle(int idleCount, boolean always) throws Exception {
if (idleCount < 1 || isClosed() || (!always && !idleObjects.hasTakeWaiters())) {
return;
}
while (idleObjects.size() < idleCount) {
PooledObject<T> p = create();
if (p == null) {
// Can't create objects, no reason to think another call to
// create will work. Give up.
break;
}
if (getLifo()) {
idleObjects.addFirst(p);
} else {
idleObjects.addLast(p);
}
}
if (isClosed()) {
// Pool closed while object was being added to idle objects.
// Make sure the returned object is destroyed rather than left
// in the idle object pool (which would effectively be a leak)
clear();
}
}
修改 Jar 版本,配置中心增加 vivo.cache.depend.common.poolConfig.timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis(检查一次连接池中空闲的连接,把空闲时间超过 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis 毫秒的连接断开,直到连接池中的连接数到 minIdle 为止)。
vivo.cache.depend.common.poolConfig.minEvictableIdleTimeMillis(连接池中连接可空闲的时间,毫秒)两个参数,重启服务后,连接池正常预热,最终从 Redis 层面上解决问题。
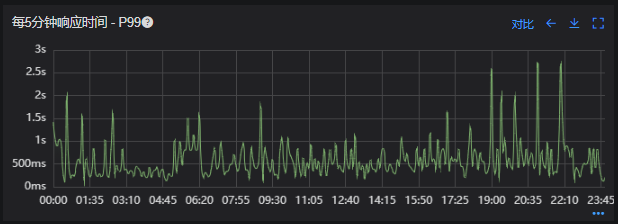
优化结果如下,性能问题基本得到解决;
Redis 响应时间(优化前)
接口 99 线(优化前)
五、总结
出现线上问题时,首先要考虑的还是快速恢复线上业务,将业务的影响度降到最低,所以针对线上的业务,要提前做好限流、熔断、降级等策略,在线上出现问题时能快速找到恢复方案。对公司各监控平台的熟练使用程度,决定了定位问题的速度,每个开发都要把熟练使用监控平台(机器、服务、接口、DB 等)作为一个基本能力。
Redis 出现响应慢时,可以优先从 Redis 集群服务端(机器负载、服务是否有慢查询)、业务代码(是否有 BUG)、客户端(连接池配置是否合理)三个方面去排查,基本上能排查出大部分 Redis 慢响应问题。
Redis 连接池在系统冷启动时,对连接池的预热,不同 commons-pool2 的版本,冷启动的策略也不同,但都需要配置 minEvictableIdleTimeMillis 参数才会生效,可以看下 common-pool2 官方文档,对常用参数都做到心中有数,在问题出现时能快速定位。
连接池默认参数在解决大流量的业务上稍显乏力,需要针对大流量场景进行调优处理,如果业务上流量不是很大直接使用默认参数即可。
具体问题要具体分析,不能解决问题的时候要变通思路,通过各种方法去尝试解决问题。
作者:vivo 互联网服务器团队-Wang Shaodong
本文文字及图片出自 InfoQ





共有{1}条精彩评论