将你的C语言代码编译成.NET
我在和我的朋友,OrangeC / C ++ 编译器的创造者,David 交流的时候,我给他出了个主意,那就是为你的编译器创建一个新的后端来生成 CLR 代码,这样一来,就没有生成 CLR 代码的C语言开源编译器了。
通常情况下,对于那些使用C语言编程并开始用C#/ VB 或一些其他的用于 .NET 的编译语言编程,那么他们希望或者甚至是需要调用我们用C语言编写的函数代码。
每当我在互联网上钻研,或说要在编译器中使用 Visual C ++ 与/clr ,或使用pInvoke来调用C语言函数,都有这样的心情。
所以我在和我的朋友,OrangeC / C ++ 编译器的创造者,David 交流的时候,我给他出了个主意,那就是为你的编译器创建一个新的后端来生成 CLR 代码,这样一来,就没有生成 CLR 代码的C语言开源编译器了。
在分离生成 x86 代码的编译器后端后,新的后端的开发在一些修复和实现之后开始了,我们已经成功取得编译器 SQLite3 并使用 DLL 与 C# 代码一起编译。
C / C ++ 编译器和到 MSIL 后端的链接
你可以遵循 OrangeC / C ++ 编译器的开发,或致力于以下链接的项目贡献:
- 官方网站:https://ladsoft.tripod.com/index.html
- GitHub 上的 OrangeC / C ++ 编译器和工具链:https://github.com/LADSoft/OrangeC
- github 上 MSIL 的 OrangeC 后端:https://github.com/LADSoft/Simple-MSIL-Compiler
构建 Orangec 编译器和用于 MSIL 的 Orangec
要构建 MSIL 的 Orange C 编译器,你需要下载 OrangeC 编译器的完整代码,你可以在这里得到源代码:
或者
在你下载源代码后,在C:\orangec 解压所有 zip 文件,在解压所有文件后,你需要下载 MSIL 后端
解压所有文件到文件夹C:\orangec\src\occ,当出现替代选项的时候,接受替代文件。
要构建和生成源代码,必须具备下面其中一个编译器:
- MinGW
- Borland C / C ++ 5.5(我用这个编译器来构建编译程序)
- CLang
- Visual C / C ++ 10
- OrangeC 编译器
在下载和解压所有文件后,打开CMD导航到文件夹C:\orangec\src,type,config.bat,在执行 config.bat,type 后:
- omake fullbuild
这将建立所有的 orangec 编译器。
构建后,也许你会看到一个关于创建 zip 文件的错误,但是不要担心。
好了,现在你已经编译好了所有的 OrangeC / C ++ 工具链,为了构建后端到 MSIL,你需要去到文件夹C:\orangec\src\occ\netil,在这个文件夹里面,type(在系统路径中具备ILASM 和CSC (C#编译器)编译器时必须的):
- omake netlib.lib
- omake
在执行这一命令后,你就有了 occil.exe
使用 OrangeC 编译器来生成 MSIL 代码
要使用编译器,你只需下载这篇文章中提供的链接,创建文件夹C:\orangec,解压该文件夹中的所有 zip 内容,打开 CMD,然后导航到C:\orangec 文件夹,在 orangec 文件夹中,type,config.bat 后,当运行 config.bat 文件时,一个新的环境变量将在CMD背景下创建,因此编译器可以定位 include 文件夹。
*重点* ——在你的路径中具备 ILASM.EXE 很有必要,为了做到这一点,你有两个办法把 ILASM 放到你的路径中:
- 运行 VSVARS32.BAT
- 在你的 CMD 中执行以下命令:
PATH =C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319;%PATH%
在构建生成的 IL 代码到 EXE / DLL 时,在路径中具备 ilasm 是有必要,然而我们正在 OrangeC 中实施 oilasm。
创建一个小例子
创建一个名为“float_to_ieee754.c”的C文件,并把代码放到C文件:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
char *strrev_t(char *str)
{
char *p1, *p2;
if (!str || !*str)
return str;
for (p1 = str, p2 = str + strlen (str) - 1; p2 > p1; ++p1, --p2)
{
*p1 ^= *p2;
*p2 ^= *p1;
*p1 ^= *p2;
}
return str;
}
void floatToBinary (float f, char *str, int numeroDeBits)
{
int i = 0;
int strIndex = 0;
union
{
float f;
unsigned int i;
}u;
u.f = f;
memset (str, '0', numeroDeBits);
for (i = 0; i < numeroDeBits; i++)
{
str[strIndex++] = (u.i & (1 << 0)) ? '1' : '0';
u.i >>= 1;
}
str[strIndex] = '\0';
str = strrev_t(str);
}
int main ()
{
float input = 0.0;
const int numeroDeBits = 32;
char *str = (char*) malloc (sizeof(char) * numeroDeBits);
printf ("Type a float number to convert to binary: ");
scanf ("%f", &input);
floatToBinary (input, str, numeroDeBits);
printf ("%s\n", str);
if(str != NULL)
free (str);
return 0;
}
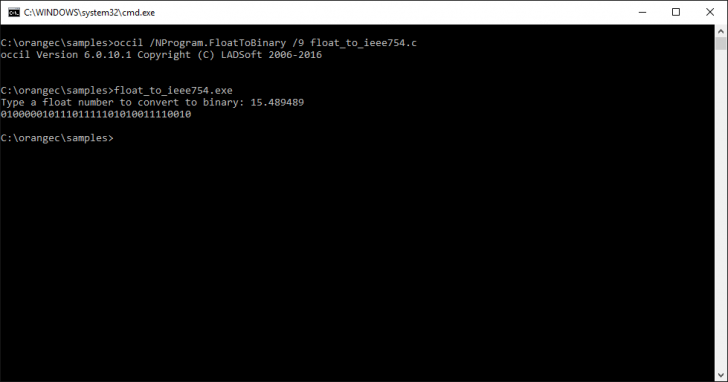
现在,为了构建代码,你需要在 CMD 中键入:
occil /NProgram.FloatToBinary /9 float_to_ieee754.c
每个参数的说明:
/N<NameSpace>.<Class>/9: C99 mode
在执行此命令后,编译器将生成指向你的代码的 IL 代码和 occil 调用 ilasm 来生成来自于 IL 代码的 EXE / DLL。如果你想看到生成的 IL 代码,只要看看你的C代码所在的文件夹,打开“float_to_ieee754.il”。
生成 IL 代码:
//File float_to_ieee754.il
//Compiler version MSIL Compiler
.corflags 3 // 32-bit
.assembly float_to_ieee754 { }
.assembly extern mscorlib { }
.assembly extern lsmsilcrtl { }
.namespace 'Program' {
.class public explicit ansi sealed 'FloatToBinary' {
.field public static valuetype 'Program.FloatToBinaryøint8[]' 'L_3' at $L_3
.data $L_3 = bytearray (25 73 a 0
)
.field public static valuetype 'Program.FloatToBinaryøint8[]' 'L_2' at $L_2
.data $L_2 = bytearray (25 66 0
)
.field public static valuetype 'Program.FloatToBinaryøint8[]' 'L_1' at $L_1
.data $L_1 = bytearray (54 79 70 65 20 61 20 66
6c 6f 61 74 20 6e 75 6d
62 65 72 20 74 6f 20 63
6f 6e 76 65 72 74 20 74
6f 20 62 69 6e 61 72 79
3a 20 0
)
.method public hidebysig static int32 'main'(int32 'argc', void * 'argv') cil managed
{
// Line 43: int main ()
.maxstack 3
.locals (
[0] float32 'input/0',
[1] void* 'str/1'
)
L_4:
// Line 45: float input = 0.0;
ldloca 'input/0'
ldc.r4 0.0
stind.r4
// Line 46: const int numeroDeBits = 32;
ldloca 'str/1'
ldc.i4 32
conv.u4
call void* [lsmsilcrtl]lsmsilcrtl.rtl::malloc (uint32)
stind.i4
// Line 48: printf ("Type a float number to convert to binary: ");
ldsflda valuetype 'Program.FloatToBinaryøint8[]' Program.FloatToBinary::L_1
call vararg int32 'printf'(void*, ...)
pop
// Line 49: scanf ("%f", &input);
ldsflda valuetype 'Program.FloatToBinaryøint8[]' Program.FloatToBinary::L_2
ldloca 'input/0'
call vararg int32 'scanf'(void*, ..., void*)
pop
// Line 50: floatToBinary (input, str, numeroDeBits);
ldloc 'input/0'
ldloc 'str/1'
ldc.i4 32
call void Program.FloatToBinary::'floatToBinary'(float32, void*, int32)
// Line 51: printf ("%s\n", str);
ldsflda valuetype 'Program.FloatToBinaryøint8[]' Program.FloatToBinary::L_3
ldloc 'str/1'
call vararg int32 'printf'(void*, ..., void*)
pop
// Line 52: if (str != NULL)
ldloc 'str/1'
brfalse 'L_7'
// Line 53: free (str);
ldloc 'str/1'
call void [lsmsilcrtl]lsmsilcrtl.rtl::free (void*)
L_7:
// Line 54: return 0;
ldc.i4 0
// Line 55: }
L_5:
ret
}
.method public hidebysig static void* 'strrev_t'(void* 'str' ) cil managed
{
// Line 5: char *strrev_t(char *str)
.maxstack 4
.locals (
[0] void* 'p1/0',
[1] void* 'p2/1'
)
L_17:
// Line 7: char *p1, *p2;
// Line 9: if (!str || !*str)
ldarg 'str'
brfalse 'L_37'
ldarg 'str'
ldind.i1
brtrue 'L_20'
L_37:
// Line 10: return str;
ldarg 'str'
br 'L_18'
L_20:
ldarg 'str'
stloc 'p1/0'
ldarg 'str'
call uint32 'strlen'(void*)
ldarg 'str'
add
ldc.i4 1
sub
stloc 'p2/1'
br 'L_26'
L_25:
// Line 12: {
// Line 13: *p1 ^= *p2;
ldloc 'p1/0'
ldloc 'p1/0'
ldind.i1
ldloc 'p2/1'
ldind.i1
xor
stind.i1
// Line 14: *p2 ^= *p1;
ldloc 'p2/1'
ldloc 'p2/1'
ldind.i1
ldloc 'p1/0'
ldind.i1
xor
stind.i1
// Line 15: *p1 ^= *p2;
ldloc 'p1/0'
ldloc 'p1/0'
ldind.i1
ldloc 'p2/1'
ldind.i1
xor
stind.i1
L_28:
ldloc 'p1/0'
ldc.i4 1
add
stloc 'p1/0'
ldloc 'p2/1'
ldc.i4 1
sub
stloc 'p2/1'
// Line 11: for (p1 = str, p2 = str + strlen (str) - 1; p2 > p1; ++p1, --p2)
L_26:
ldloc 'p2/1'
ldloc 'p1/0'
bgt 'L_25'
L_27:
// Line 16: }
ldarg 'str'
// Line 18: }
L_18:
ret
}
.method public hidebysig static void 'floatToBinary'(float32 'f' ,
void* 'str' , int32 'numeroDeBits' ) cil managed
{
// Line 20: void floatToBinary (float f, char *str, int numeroDeBits)
.maxstack 4
.locals (
[0] int32 'i/0',
[1] int32 'strIndex/1',
[2] valuetype 'Program.FloatToBinaryø__anontype_2486130647_0' 'u/2'
)
L_41:
// Line 22: int i = 0;
ldloca 'i/0'
ldc.i4 0
stind.i4
// Line 23: int strIndex = 0;
ldloca 'strIndex/1'
ldc.i4 0
stind.i4
// Line 29: u.f = f;
ldloca 'u/2'
ldarg 'f'
stind.r4
// Line 30: memset (str, '0', numeroDeBits);
ldarg 'str'
ldc.i4 48
ldarg 'numeroDeBits'
conv.u4
call void* 'memset'(void*, int32, uint32)
pop
// Line 31:
ldc.i4 0
stloc 'i/0'
br 'L_45'
L_44:
// Line 33: {
// Line 34: str[strIndex++] = (u.i & (1 << 0)) ? '1' : '0';
ldloc 'strIndex/1'
ldarg 'str'
add
ldloc 'strIndex/1'
ldc.i4 1
add
stloc 'strIndex/1'
ldloca 'u/2'
ldind.u4
ldc.i4 1
and
brfalse 'L_56'
ldc.i4 49
br 'L_57'
L_56:
ldc.i4 48
L_57:
conv.i1
stind.i1
// Line 35: u.i >>= 1;
ldloca 'u/2'
ldloca 'u/2'
ldind.u4
ldc.i4 1
shr.un
stind.i4
L_47:
ldloc 'i/0'
ldc.i4 1
add
stloc 'i/0'
// Line 32: for (i = 0; i < numeroDeBits; i++)
L_45:
ldloc 'i/0'
ldarg 'numeroDeBits'
blt 'L_44'
L_46:
// Line 36: }
ldloc 'strIndex/1'
ldarg 'str'
add
ldc.i4 0
stind.i1
// Line 39:
ldarg 'str'
call void* Program.FloatToBinary::'strrev_t'(void*)
starg 'str'
// Line 41: }
L_42:
ret
}
.field public static void *'__stdin'
.field public static void *'__stdout'
.field public static void *'__stderr'
.field public static void *'_pctype'
.method private hidebysig static void '$Main'() cil managed {
.entrypoint
.locals (
[0] int32 'argc',
[1] void * 'argv',
[2] void * 'environ',
[3] void * 'newmode'
)
.maxstack 5
call void *'__pctype_func'()
stsfld void * Program.FloatToBinary::_pctype
call void *'__iob_func'()
dup
stsfld void * Program.FloatToBinary::__stdin
dup
ldc.i4 32
add
stsfld void * Program.FloatToBinary::__stdout
ldc.i4 64
add
stsfld void * Program.FloatToBinary::__stderr
ldloca 'argc'
ldloca 'argv'
ldloca 'environ'
ldc.i4 0
ldloca 'newmode'
call void __getmainargs (void *, void *, void *, int32, void *);
ldloc 'argc'
ldloc 'argv'
call int32 Program.FloatToBinary::main (int32, void *)
call void exit (int32)
ret
}
.class nested private value explicit ansi sealed 'int8[]' {.pack 1 .size 1}
.class nested public value explicit
auto sequential ansi sealed '__anontype_2486130647_0' {.pack 4 .size 4}
.class nested public value explicit auto sequential ansi sealed 'int32[2]' {.pack 1 .size 8 }
.class enum nested public auto ansi sealed 'orient' {
.field public static literal valuetype Program.FloatToBinary/orient __or_unspecified = int32(0)
.field public static literal valuetype Program.FloatToBinary/orient __or_narrow = int32(1)
.field public static literal valuetype Program.FloatToBinary/orient __or_wide = int32(2)
.field public specialname rtspecialname int32 value__
}
}
}
.method private hidebysig static void * __GetErrno () cil managed {
.maxstack 1
call void * '_errno'()
ret
}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl ("msvcrt.dll" cdecl)
void* 'memset'(void*, int32, uint32) preservesig {}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl (".dll" cdecl)
uint32 'strlen'(void*) preservesig {}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl ("msvcrt.dll" cdecl)
vararg int32 'scanf'(void*) preservesig {}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl ("msvcrt.dll" cdecl)
void 'exit'(int32) preservesig {}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl ("msvcrt.dll" cdecl)
vararg int32 'printf'(void*) preservesig {}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl ("msvcrt.dll" cdecl)
void '__getmainargs'(void*, void*, void*, int32, void*) preservesig {}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl ("msvcrt.dll" cdecl)
void* '__pctype_func'() preservesig {}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl ("msvcrt.dll" cdecl)
void* '_errno'() preservesig {}
.method public hidebysig static pinvokeimpl ("msvcrt.dll" cdecl)
void* '__iob_func'() preservesig {}
为了执行生成的 EXE / DLL,有两个可执行的 DLL 很有必要,这样你可以在C:\orangec\bin\中得到这两个 DLL,你只要复制 DLL 到相同 EXE 文件夹,并执行生成的 EXE。
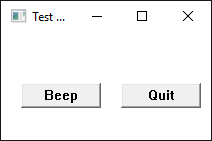
构建一个简单的 GUI 应用程序
编译器还不支持所有创建有 Windows GUI 的复杂程序,但可以编译简单程序,在这个例子中,让我们创建一个简单的窗口。
*注*:为了编译代码来使用图形界面,此时我们仍然需要声明主要部分。
在这个简单的示例中,我们创建了一个C文件,叫做:window.c
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
const char g_szClassName[] = "WindowClass";
void createButtons (HWND hwnd)
{
CreateWindow ("button", "Beep",
WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD,
20, 50, 80, 25,
hwnd, (HMENU)1, NULL, NULL);
CreateWindow ("button", "Quit",
WS_VISIBLE | WS_CHILD,
120, 50, 80, 25,
hwnd, (HMENU)2, NULL, NULL);
}
LRESULT CALLBACK WndProc (HWND hwnd, UINT msg, WPARAM wParam, LPARAM lParam)
{
switch (msg)
{
case WM_CREATE:
createButtons (hwnd);
break;
case WM_COMMAND:
{
if (LOWORD (wParam) == 1)
Beep (40, 50);
if (LOWORD (wParam) == 2) {
MessageBox (hwnd, "Goodbye, cruel world!", "Note", MB_OK);
PostQuitMessage (0);
}
break;
}
case WM_CLOSE:
DestroyWindow (hwnd);
break;
case WM_DESTROY:
PostQuitMessage (0);
break;
default:
return DefWindowProc (hwnd, msg, wParam, lParam);
}
return 0;
}
int WINAPI WinMain (HINSTANCE hInstance, HINSTANCE hPrevInstance, LPSTR lpCmdLine, int nCmdShow)
{
WNDCLASSEX wc;
HWND hwnd;
MSG Msg;
wc.cbSize = sizeof(WNDCLASSEX);
wc.style = 0;
wc.lpfnWndProc = WndProc;
wc.cbClsExtra = 0;
wc.cbWndExtra = 0;
wc.hInstance = hInstance;
wc.hIcon = LoadIcon (NULL, IDI_APPLICATION);
wc.hCursor = LoadCursor (NULL, IDC_ARROW);
wc.hbrBackground = (HBRUSH)(COLOR_WINDOW + 1);
wc.lpszMenuName = NULL;
wc.lpszClassName = g_szClassName;
wc.hIconSm = LoadIcon (NULL, IDI_APPLICATION);
if (!RegisterClassEx (&wc))
{
MessageBox (NULL, "Window Registration Failed!", "Error!",
MB_ICONEXCLAMATION | MB_OK);
return 0;
}
hwnd = CreateWindowExA (
WS_EX_CLIENTEDGE,
g_szClassName,
"Test window in .Net!! :) ",
WS_OVERLAPPEDWINDOW,
CW_USEDEFAULT, CW_USEDEFAULT, 230, 150,
NULL, NULL, hInstance, NULL);
if (hwnd == NULL)
{
MessageBox (NULL, "Window Creation Failed!", "Error!",
MB_ICONEXCLAMATION | MB_OK);
return 0;
}
ShowWindow (hwnd, nCmdShow);
UpdateWindow (hwnd);
while (GetMessage (&Msg, NULL, 0, 0) > 0)
{
TranslateMessage (&Msg);
DispatchMessage (&Msg);
}
return Msg.wParam;
}
int main (int argc, char* argv[])
{
STARTUPINFOA si;
GetStartupInfoA (&si);
int ret = WinMain (GetModuleHandleA (NULL), NULL, "", (si.dwFlags & 1) ? si.wShowWindow : 10);
return ret;
}
要生成这个源代码,报告编译器 libs. 在源中使用了什么是必要的,因此,在命令行中生成源代码是这样的:
occil /Lkernel32 /Luser32 /9 window.c
生成之后,我们就可以执行应用程序: )

在 C# 中创建并使用来自于C语言代码的 DLL
现在我们知道如何从C语言代码创建一个 .NET EXE。下面让我们从C语言代码创建一个 DLL,并和你的 C# 代码一起使用它。
用C语言创建一个简单的堆栈,为此,创建一个名为“stack.c”的C文件,并在文件中插入下面的代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct _stack_
{
int size;
int totalitems;
int* stack;
} stack;
stack* pl_initastack (int size);
void pl_push (stack* pl, int elemento, int* success);
int pl_pop (stack* pl, int* success);
int pl_top (stack *pl, int* success);
int pl_base (stack* pl, int *success);
int pl_stackfull (stack* pl);
int pl_stackempty (stack* pl);
void pl_freestack (stack *pl);
void pl_cleanstack (stack *pl);
stack* pl_initastack (int size)
{
stack* pl = (stack*) malloc (sizeof(stack));
pl->stack = (int*) malloc (sizeof(int) * size);
pl->size = size;
pl->totalitems = 0;
return pl;
}
void pl_push (stack* pl, int elemento, int* success)
{
if (!pl_stackfull (pl))
pl->stack[pl->totalitems++] = elemento;
else
*success = 0;
}
int pl_pop (stack* pl, int* success)
{
if (!pl_stackempty (pl))
{
*success = 1;
return pl->stack[--pl->totalitems];
}
else
{
*success = 0;
return -1;
}
}
int pl_top (stack *pl, int* success)
{
if (pl_stackempty (pl))
{
*success = 0;
return -1;
}
else
{
*success = 1;
return pl->stack[pl->totalitems - 1];
}
}
int pl_base (stack* pl, int *success)
{
if (pl_stackempty (pl))
{
*success = 0;
return -1;
}
else
{
*success = 1;
return pl->stack[0];
}
}
int pl_stackfull (stack* pl)
{
return pl->totalitems >= pl->size;
}
int pl_stackempty (stack* pl)
{
return pl->totalitems == 0;
}
void pl_freestack (stack* pl)
{
free (pl->stack);
free (pl);
}
void pl_cleanstack (stack *pl)
{
pl->stack = malloc (sizeof(int) * pl->size);
pl->totalitems = 0;
}
现在,你需要用选项/Wd 生成这个源代码。这将告诉编译器你想要生成一个 DLL,所以为了建立这个文件,我们使用这个命令行:
occil /ostackdll.il /c /Wd /9 /NStackLib.Stack stack.c
建立 stack.c 后,让我们构建生成的 IL 代码到 DLL:
ilasm /DLL stackdll.il
现在,让我们创建 C# 项目。在这篇文章中,我创建了一个 .NET 4.0 的 C# 项目。
对此,你可以使用 OCC 生成的 DLL,你需要在 C# 项目中做一些设置:
- Enable Unsafe code
- Plataform target: x86
在设置这些选项后,在引用中添加 stack.dll,并写代码来使用 DLL,在这种情况下,我写了这个简单的示例程序:
using System;
namespace Stack
{
unsafe class Program
{
static void Main (string[] args)
{
void* stk = null;
stk = StackLib.Stack.pl_initastack (5);
int success = 1;
Console.WriteLine ("Pushing values to stack...");
for(int i=0; (success == 1); i++)
{
int val = i * 10;
StackLib.Stack.pl_push (stk, val, &success);
}
Console.WriteLine ("Base value in stack: {0}", StackLib.Stack.pl_base (stk, &success));
Console.WriteLine ("Top value in stack.: {0}", StackLib.Stack.pl_top (stk, &success));
Console.WriteLine ("Poping values from stack");
while(true)
{
int val = StackLib.Stack.pl_pop (stk, &success);
if (success == 0)
break;
Console.WriteLine ("{0}", val);
}
StackLib.Stack.pl_freestack (stk);
stk = null;
}
}
}
在你构建 EXE 后,不要忘了复制在 orangec 文件夹的 BIN 文件夹中的两个 DLL。

使用 SQLite
现在我们知道如何在C语言中创建并使用来自于源代码的 DLL,让我们使用 SQLite!
你可以在文件夹 \samples\sqlite3中找到 SQLite 源代码。
要构建 SQLite 源代码,有必要使用此命令行:
occil /9 /Wd /Lkernel32 sqlite3.c /Nsqlite3.sqlite
在建立 SQLite 后,创建一个 C# 或任何其他 .NET 项目,随你选择,在项目中添加 SQLite 的编译 DLL 的引用,设置项目类型为 x86 以及在必要时启用不安全模式,在我的情况中,我创建了一个简单的 C# 项目,并随便弄了个小程序来使用 SQLite:
using System;
using System.IO;
using sqlite3;
using lsmsilcrtl;
namespace sqliteil
{
unsafe class Program
{
static string[] Names { get; } = new string[]
{
"Bob",
"Tom",
"Carlos",
"Marcos",
"Alexandre",
"Alex",
"Morgana",
"Maria",
"Jose",
"Joao",
"Marcos",
"Gustavo",
"Roberto",
"Rodrigo",
"Teste"
};
static int Main (string[] args)
{
String dbName = "dbtest.db";
if (File.Exists (dbName))
File.Delete (dbName);
void* db;
// Create the database
int rc = sqlite.sqlite3_open (CString.ToPointer (dbName), &db);
if (rc != 0)
{
Console.WriteLine ("Fail to create the database : (");
return -1;
}
// Create the table
void* stmt;
sqlite3.sqlite.sqlite3_prepare_v2(db, CString.ToPointer ("CREATE TABLE demo (name TEXT, age INTEGER);"), -1, &stmt, null);
rc = sqlite.sqlite3_step (stmt);
if (rc != 101)
{
Console.WriteLine ("Fail to create the table : (");
return -1;
}
sqlite.sqlite3_finalize (stmt);
// Insert some data in table
foreach (var name in Names)
{
var insertLine = String.Format ("insert into demo (name, age) values ('{0}', {1});", name, new Random () .Next (1, 99));
var query = CString.ToPointer (insertLine);
sqlite.sqlite3_prepare_v2(db, query, insertLine.Length, &stmt, null);
rc = sqlite.sqlite3_step (stmt);
if (rc != 101)
{
Console.WriteLine ("Fail to insert the name: {0}", name);
}
sqlite.sqlite3_finalize (stmt);
}
// Read the inserted data...
var select = "SELECT * FROM demo;";
rc = sqlite.sqlite3_prepare_v2(db, CString.ToPointer (select), select.Length, &stmt, null);
if(rc == 0)
{
bool done = false;
while(!done)
{
switch(rc = sqlite.sqlite3_step (stmt))
{
case 5:
case 101:
done = true;
break;
case 100:
{
string name = new CString (sqlite.sqlite3_column_text (stmt, 0)) .ToString ();
int age = sqlite.sqlite3_column_int (stmt, 1);
Console.WriteLine ("Name: {0} -- Age: {1}", name, age);
rc = 0;
}
break;
default:
done = true;
break;
}
}
}
sqlite.sqlite3_close (db);
return 0;
}
}
}
该项目在 SQLite 测试文件夹内。

本文由 TecHug 分享,英文原文及文中图片来自 www.codeceo.com。
你也许感兴趣的:
- 微软:重新构想 .NET 的构建与发布方式(再次)
- .NET 10 有哪些新特性?你对.NET 10 的计划是什么?是迁移还是暂缓?
- .NET 10 性能优化
- 微软 .NET 10 发布首个预览版
- 【外评】Ubuntu 24.04 中 .NET 的新功能
- 【外评】使用 .NET Core 开发软件的 9 大优势
- 【译论】是 .net 遥遥领先,还是我有幻觉?
- 开发者阵营分化,.NET 开源生态系统如何走向未来?
- .NET 8.0中有哪些新的变化?
- Csharp 不停止膨胀,必将走向灭亡


你对本文的反应是: